- Home
- Company
- Amino Acid Encyclopedia
- Power of Amino Acids! We Use Them Every Day!
- Amino Acids and Calorie Reduction
Amino Acids and Calorie Reduction
Aspartame—Natural Sweetness and Low in Calories

![]()
-
Aspartame is a high intensity sweetener made from amino acids.
Aspartame is safe and approved for consumption in more than 125 countries and regions worldwide.
![]()
A High Intensity Sweetener Made from Amino Acids,
Safe to Consume
Aspartame is Made From Amino Acids, which Make up Proteins
Each amino acid has its own taste. These amino acids can be combined to produce new tastes and functions.
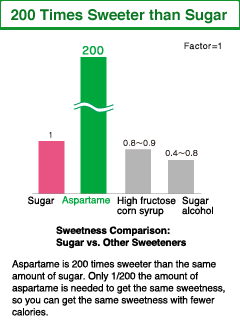
Aspartate has a sour taste with slight umami, while phenylalanine has a bitter taste. Aspartame is made by binding Aspartate and phenylalanine to produce a high intensity sweetener that is 200 times sweeter than sugar.
Aspartame is made from amino acids, the same amino acids that make up the proteins from familiar foods such as meats, dairy products, grains and vegetables. In the body, aspartame is broken down into amino acids, which makes its consumption safe.
Natural sweetness similar to sugar
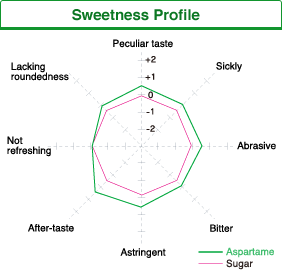
Aspartame has a similar sweetness profile to sugar. Compared with other high intensity sweeteners aspartame does not have a peculiar taste or bitterness. It has a natural sweetness that enhances the flavor of food.
Aspartame—Approved in Over 125 Countries and
Regions Worldwide
The safety of aspartame has been repeatedly demonstrated and the research thoroughly tested. These tests show that aspartame is safe to consume.
The aspartame has been approved as safe for consumption in over 125 countries and regions worldwide. This includes the United States, Europe, Asia, and Africa. The Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA)*1, an international body, has set the acceptable daily intake (ADI)*2 of aspartame at 40 milligrams per kilogram of body weight. In Japan the Minister of Health and Welfare (now Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare) designated aspartame as a food additive after a review by the Food Sanitation Council.
*1 The Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) is administered by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
*2 The acceptable daily intake (ADI) is the maximum amount of a food additive that a person can ingest on a daily basis over a lifetime without negative health effects.
Aspartame FAQs
What amino acids are used to make aspartame?
How is aspartame made?
Aspartame is an amino acid-based sweetener that is 200 times sweeter than sugar. Aspartame is made from Aspartate and phenylalanine, which are found in many foods and proteins.
Aspartame is made by forming peptide bonds of Aspartate and phenylalanine. It is then refined and dried.
These peptide bonds are also formed when amino acids are made into proteins. The amino acids in aspartame are digested, absorbed, metabolized and excreted just like the amino acids in regular foods.
Is aspartame proven safe?
Aspartame has been deemed safe after extensive and thorough review of available research by JECFA, an international body, as well as the United States Food & Drug Administration (FDA) and Food Sanitation Council of Japan.
The FDA has stated that "Aspartame is one of the most exhaustively studied substances in the human food supply."
(http://www.fda.gov/Food/IngredientsPackagingLabeling/FoodAdditivesIngredients/ucm397725.htm)
In the review by the Scientific Committee on Food (SCF) of the European Union in 2002 the committee declared that "Aspartame is unique among the intense sweeteners in that the intake of its component parts can be compared with intakes of the same substances from natural foods."
(https://ec.europa.eu/food/sites/food/files/safety/docs/sci-com_scf_out155_en.pdf)
Aspartame is currently approved for consumption in over 125 countries and regions worldwide including in the United States, Canada, United Kingdom and France.
Can aspartame be safely consumed every day?
It is completely safe to consume aspartame in your daily diet. If, instead of sugar, a person were to consume the same amount of aspartame (based on relative sweetness) a person who weighs 50 kilograms (110 pounds) would on average consume just 1/5 the acceptable daily intake (ADI) in the United States, 2/7 the ADI in the European Union, and 1/6 the ADI in Japan.
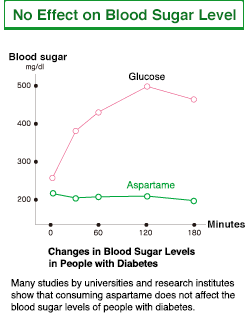
Does aspartame affect blood sugar levels?
Will I lose weight if I switch from sugar to aspartame?
Aspartame is digested, absorbed, metabolized, and excreted in the body as amino acids. It has no effect on blood sugar levels. Aspartame is different from sugar and it is used in small amounts, so it doesn’t stimulate the secretion of insulin.
Consuming aspartame can reduce your overall calorie intake. However, switching from sugar to aspartame by itself will not make you lose weight.
Is it safe to consume aspartame while pregnant or breastfeeding?
Will extended consumption of aspartame affect a child's growth?
Aspartame is digested, absorbed, metabolized and excreted just like amino acids in regular foods. Women can safely consume aspartame while pregnant or breastfeeding.
Studies show that even if three times the accepted daily allowance of aspartame is consumed, there is no effect. Studies have also shown that aspartame is safe for children to regularly consume.

